
 |
|
#1
|
||||
|
||||
|
in japan
CS-PCM audio broadcast is a digital audio broadcast that was broadcast using communication satellites , and was a type of satellite digital radio. 目次 Summary Broadcasting started in June 1992. At the beginning, it was broadcast on a total of 18 channels: 2 satellites, 6 companies and 3 stations for each station. The tuner was 180,000 yen for the NE-PCM 9000 released by NEC Home Electronics at the same time the broadcast started. In Japan, broadcast was finally performed using 10 channels by Music Bird , but the broadcast ended on July 31, 2011. The sampling frequency of voice is 48 kHz or 32 kHz. The scrambling method was the core tech method. from reorganization to end Due to sluggish sales due to the recession of the bubble economy and stagnation in the number of subscriptions itself, another company merged one after another when PCM Japan and PCM Central were shut down in June 1993, one year later. It becomes only a music bird in October, 1996. The music bird also announced the end of the PCM audio broadcast on July 31, 2011, and then the broadcast ended as scheduled. The reason is that due to the termination of the production of the chip for encryption, additional production of tuners is not possible, and the encryption work of the consignee (Broadcast Security Center) is finished [1] . This caused all CS-PCM audio broadcasts to disappear. It is the same time as the end of analog BS broadcasting in Japan. (Musicbird is currently broadcasting on SPACE DiVA.) History From June 1992, six consignment broadcasters started to broadcast three channels each in turn. company name Nickname Use satellite Used channel number Broadcast start date Remarks PCM Japan Co., Ltd. SOUND AIR PJ Superbird B S-10 June 15, 1992 Nippon Television System PC M Zipang Communications Inc. PCM-ZIPANG JC-SAT2 J-6 June 18, 1992 TBS system Music Bird Inc. MUSIC BIRD JC-SAT2 J-8 August 3, 1992 TOKYO FM system Satellite Music Inc. JC-SAT2 J-8 August 3, 1992 Daiei (current ・Kadokawa movie ) system Nippon Music Congress Co., Ltd. RADIO SKY JC-SAT2 J-6 August 18, 1992 Japanese Herald movie (now Kadokawa movie) PC-M Central Co., Ltd. PCM Central Superbird B S-10 September 1, 1992 Chubu Nippon Broadcasting System June 4, 1993 PCM Japan, PCM Central finished broadcasting, business was discontinued on July 1. The broadcast on Superbird B disappears. October 1st, 1994 PCM Zipang Communications and Nippon Music Congress merged and opened as Zipang & Sky Communications Inc. (PCM Z-SKY). July 1, 1995 Satellite music merged with Music Bird. Oct. 1, 1996 Zipang & Sky Communications merged with Music Bird. June 1, 2002 Musicbird shifts to the Telecommunications service utilization broadcasting business for PCM voice broadcasting. July 31, 2011 Musicbird stops PCM voice broadcasting. All PCM audio broadcasts in Japan disappeared on the same day. (The satellite used is JC-SAT2A from June 2002)   The multiband tuner in which it corresponded to a satellite broadcasting, a terrestrial TV broadcast, and FM and AM, and also the timer was carried. The multiband tuner in which it corresponded to a satellite broadcasting, a terrestrial TV broadcast, and FM and AM, and also the timer was carried.1 bitD/A converter of a bit stream scheme which had adopted the PLL synthesizer scheme as the BS tuner part, and Philips developed in the PCM speech-signal-processing circuitry -- an adoption bookmark -- the quality tone quality is realized. An image/voice carries two lines in an output-terminal, and also the digitized voice output also carries two lines, light and a coaxial. The mode setting of television / independent voice, and a main/factice is separately possible for the voice output of digital one and an analog respectively. Moreover, the input/output terminal for high-visions is also carried. The U/V all band voice multiplex PLL synthesizer is adopted as TV tuner part. a split carrier -- since a scheme, it excelled in the receiving performance by the high sensitivity, and the high image of a quality has been realized. Moreover, the front end as which ST-50 was adopted is carried in FM tuner part. 12 games are carried by BS/TV and the preset memory of 12 games is carried by FM/AM. It is possible to carry out memory also of the fine-tuning status of TV by a setups and manual of the audio mode of BS to a preset channel. A timer can be set for one week to five special NetWare programs, and can be arbitrarily set out of four variations of every day / every week runtime except "a once / every day / Saturday, and Sunday." Moreover, the sleep timer functionality is also carried and a sleep setups is also possible every 10 minutes for a maximum of 60 minutes. It is possible to use it by a cassette deck, a compact disk player, etc. with the remote-control termination of a Marantz, and interlock. The remote control only for this multifunction tuner is carried. It is combining with PM700audio video, and power-source on/off, a function switchover, etc. are possible at the interlocking functionality by a BUS line. in europe The Digital Satellite Radio ( DSR ) was the first digital radio broadcast in Germany for the listener. Unlike today's digital transmission technology, DSR did not focus on increasing the number of programs, but on improving the transmission quality. Inhaltsverzeichnis History Grundig DSR 100 (circa 1991) Revox H7 (circa 1995) The first prototype of a receiver for DSR presented the company Telefunken from 20 to 26 August 1982 at the fair HIFIVIDEO'82 in Dusseldorf. In the fall of 1984, after a cable pilot project in the same year, the decision was made for this system. On the occasion of the Internationale Funkausstellung in Berlin, Federal Post Minister Christian Schwarz-Schilling officially launched Digital Satellite Broadcasting on 24 August 1989. Via the two satellites DFS 1 Kopernikus , TV SAT 2 and the cable network of Deutsche Bundespost Telekom, a package of 16 radio programs was now available nationwide. For the reception one needed a special DSR receiver, which cost at first clearly more than 1000 DM. For satellite reception, a small flat antenna with an edge length of only 30 cm was additionally required. At the end of 1994, the broadcast was switched off via satellite TV SAT 2. Thus, the program was only on the satellite Copernicus or by means of a special receiver via the cable television Telekom to receive. Rumors of the phasing out and expiry of telecoms and program providers contracts in 1996 led to prices for DSR receivers falling to around DM 200 from 1995 onwards. In total, about one to two hundred thousand DSR radios were sold. The "Round Table" on the development of cable television convened at the invitation of the then DTAG CEO Ron Sommer decided on May 20, 1997, that the special channels S2 and S3 occupied by the DSR must urgently be cleared for analog TV broadcasting. This should be done by the end of 1998. At 1:01 pm on January 16, 1999, DSR was shut down despite protests from many listeners. For receivers that were purchased after 1996, there was a compensation from the telecom. Until recently, 16 radio stations were distributed via DSR to 118 MHz (special channels 2 and 3) in the Telekom cable. K 01: Bayern 4 Classic K 02: SWF 2 / SDR 2, from 1991 S2 culture , from 30 August 1998 Südwestrundfunk 2 K 03: Radio Bremen 2 , 1991 in alternation with Deutsche Welle K 04: Hessischer Rundfunk 2 K 05: NDR 3 , from October 8, 1997 NDR Radio 3 K 06: Star * Sat Radio, from 1997 Deutschlandfunk xtra (mono) K 07: Deutschlandfunk K 08: Westdeutscher Rundfunk 3 K 09: RIAS 1, from 1994 Germany Radio Berlin K 10: SR 1 (Europawelle Saar) K 11: Radio Belcanto / Antenne Bayern , from 1991 Antenne Bayern, 1992-1993 Germany's culture , from 1994 Rhineland-Palatinate Radio 2 K 12: From 1991 classical radio K 13: From 1991 radio ffn , from 1994 RTL radio K 14: From 1991 Radioropa Info , from 1996 Radio Melody K 15: From 1992 RTL Radio , from 1994 MDR Sputnik K 16: From 1992 Radio Xanadu , from 1994 Energy Munich In an infinite loop that went well beyond January 16, 1999, the hiring of DSR was explained by Telekom as follows: "At the end of January 15, the operation of DSR has been discontinued, as previously announced several times. For more information, call 0800 3738393. " In Switzerland, the DSR under the name DigitSuperRadio for some years in some cable networks (eg the Cablecom ) was active. At times there were two packages, a German and a Swiss, with a total of 32 channels. Swisscom broadcast ceased broadcasting on 31 December 2003. Last 15 stations were still receivable. The successors of DSR A substitute broadcast via satellite of the originally distributed by DSR radio station was carried out in analog transponders by ADR and digital transponders by DVB-S . Until March 1999, except for SWR 2 and SR 1, all former DSR stations of public service broadcasting had to be received digitally as DVB-C in Deutsche Telekom's cable TV in the ARD and ZDF bouquets. The bit rate of the now compressed digital mode was 192 kBit / s. To receive these offers, however, a new hardware was required (eg d-box II), because the DSR tuners are not suitable for receiving the ADR or DVB-S signals. However, ADR was shut down on April 30, 2012 along with the shutdown of the analog TV and radio programs. On 19 August 2005, two weeks before the radio exhibition in Berlin, virtually all ARD radio programs in the DVB-S standard could be received via satellite Astra 19.2 ° East. The bit rate of the stereo programs distributed in MP2 amounts to 320 kBit / s, of which at least 256 kBit / s are used for audio data. The rest can (but does not have to) be used for additional data (RDS-like features, Radio Screen Show RaSS). Although in contrast to DSR the MP2 transmission is psychoacoustically data-reduced, at least theoretically at 320 kBit / s a very high sound quality is guaranteed. Coding artifacts are inherent in principle, but should not be acoustically noticeable in clean implementation, however, at the very high bit rates. In addition, selected programs on some of the ARD culture waves are also available in Dolby 5.1 - something that was not possible with DSR. The dynamics processing ("sound processing") is at individual institutions on the 5.1-track significantly more moderate to none at all, so that here again a higher-tonal transmission path results. In most cable networks, the ARD-DVB radio programs are now also offered in the DVB-C standard, so that a largely nationwide coverage (satellite and cable) is guaranteed with high-quality digital radio. The advantages over DSR are in particular the much larger variety of programs, the possibility of 5.1 surround sound and the direct digital recording on USB storage devices connected to suitable receivers or directly on receivers (PVR) built-in hard drives. Of more "academic" nature is the benefit that results from using a sampling rate of 48 kHz. While with DSR (sampling rate 32 kHz) an upper audio cutoff frequency of approx. 15 kHz existed, with 48 kHz sampling rate quite possibly 20 to 22 kHz upper cutoff frequency are possible, so the programs are provided accordingly and not sound-processed. For a long time, with the exception of a single, very expensive DVB radio receiver, there were no pure DVB receivers on the market that can be set up, maintained and programmed without a connected monitor. DSR tuners were always fully operable on the device with the aid of its display, the first DVB receivers designed primarily for TV use always require an image output for menu operation. With the shutdown of the analog signal in the cable, the situation improved and DVB tuners appeared, which can be operated and adjusted independently of a picture output. The disadvantage over DSR is in principle the use of a psychoacoustic data reduction with the associated artifacts. Technique Compared to ADR , DAB or DVB , which work with data reduction, was waived at DSR. The playback quality of DSR is comparable to an audio CD . 16 radio programs were bundled digitally via a satellite transponder broadcast and redistributed in the cable network of Deutsche Telekom to 118 MHz (cable channel S2 / 3). Other data was being transmitted parallel to the music: There was a voice / music bit that the receivers could use to adjust the volume separately for languages and music. The sender identification and the type of program such as classical music, pop music or cultural program were also transmitted. For the transmission, a sampling rate of 32 kHz was chosen, since this corresponds to the internationally agreed sampling frequency for digital audio program transmission lines. Thus, audio signals up to 15 kHz could be transmitted. At the time of planning DSR, the Deutsche Bundespost was just setting up its digital network. The combination of 30 telephone channels ( primary rate access ) resulted in a bundle with a transmission rate of 2048 kbit / s (DS2). These smallest bundles could be further grouped into higher order bundles of 8448 (DS8), 34368 (DS34), or 137472 kbps (DS140). Since 16 channels including parity bits per channel result in three channels of 1632 kBit / s, the remainder would be 288 kBit / s. By reducing the word width to 14 bits, the channel bit rate was optimally utilized. The net bit rate of a stereo signal (2 × 14 bits × 32 kHz = 896 kbit / s) reached approximately half the net bit rate (992 kbit / s) of the DS2 burst. For example, half the gross bit rate of 1024 kbps (DS1) was selected for the stereo signal. In addition, it made sense to use a similar frame structure with 256 bits. Thus, a 256-bit block consisted of 8-bit frame identifier, followed by 4 × 30-bit music data, another 8-bit additional information, and again 4 * 30-bit music data. On a DS2 line, 8000 of these blocks were transmitted per second. The 30 bits of a sample consisted of 14 bits for the left channel and 14 bits for the right channel for one stereo signal or two mono channels and one 15th parity bit each. This was taken into account with the 3-bit scale factor that was transferred in this bit. The word width of 14 bits, which was predetermined by the full utilization of the mail feeder lines, was also retained in the radio transmission. Only the DSR receiver restored the 16-bit audio signal. In the specification of the DS1 interface, an attempt was made to realize a new quality of the sound signal transmission. Quote: "With the agreement between the broadcasters and the DBP to use in the future for higher-quality sound connections DS1 Tonkanaltechnik with digital signal transmission, has certainly begun a new era of sound engineering." [1] The coding http://www.radiodesign.de/atelier/tuner.htm With a 10 dB safety margin and linear quantization characteristic with a sinusoidal signal, 14 bits result in a signal-to-noise ratio of 76 dB as a result of the quantization noise . Since you wanted to get the dynamics of 98 dB of 16 bits, you had to encode the signal. For this purpose, the signal was split into eight 6 dB wide sections. Out of every 64 consecutive samples, the maximum was taken and a 3-bit scale factor was calculated for that block. This scale factor was transmitted within the parity bits, 21 times per block. When decoded in the receiver, it was determined by majority vote. A scale factor of 1 inverts the parity bit of the corresponding word. Losses occurred only at full scale (0 dB - scale factor 0). In this case, the least significant bit or the two least significant bits were not transmitted. However, that was negligible because the upper levels served the headroom and it was assumed that they were rare. So the 16 bits of the original PCM signal could be transmitted. This 16/14 bit floating point representation was expandable for up to 18 bits per sample transfer. On the satellite link this data stream was channel coded by means of the BCH code in order to obtain the redundancy for error detection and error correction. 44 bits of useful signal were coded into a 63-bit block with corresponding redundancy information and combined in frames of 512 bits in length. This bit stream was modulated on the RF carrier by means of digital phase modulation , which can transmit two bits per transmit symbol (4-PSK). The bandwidth was 27 MHz that of a television channel. In addition to the music, information was transmitted at 11 kB / s per stereo channel.  IN AMERICAS/EUROPE/MID.EAST https://youtu.be/VpyhTl8Nky8?t=175 Look at lcd bi directional remote control the digitall sat.transm.is ALCATEL 128 DMX, a Mood Media company,[1] is a "multi-sensory" branding agency based in Austin, Texas.[2][3] DMX also provides music for cable and satellite television networks worldwide, including DStv in Africa. Contents Alcatel's MVR 128 system distributes high quality mono and stereo sound signals over a satellite video channel. Because the signals are digitized as they leave the studio and remain so until they reach the satellite signal receiver port, excellent sound quality is guaranteed. With 30 high quality stereo signals, the MVR 128 system has three times the capacity of the older MVR 20 system, with which it is still compatible History AEI Music Network Inc. was born in 1971, as a music service to license and program original artist music. AEI's primary focus was custom music programs, provided on cassette tapes for domestic and international customers. In the 1980s, the company began providing services to international airlines, as well as residential and cable television systems. AEI was the first to offer music by satellite. In 2001, AEI merged with Liberty Digital Inc. of Los Angeles, in a deal that gave Liberty 56 percent and AEI 44 percent of the merged company, known as DMX/AEI Music. AEI had large national customers into international markets, (while DMX had dealt with smaller businesses). DMX also served residential cable television subscribers, working on streaming over the Internet.[4][5][6] The company's on-site digital system known as "ProFusion" was launched in 2002 with the purpose of delivering and playing back high-quality digital music to places around the world. In 2005, DMX was purchased by Capstar Partners who then officially changed the name to DMX, Inc. It was in this year that the "ProFusion M5", its first digital platform that controls both video and music content, was launched. Most recently, the company began offering scent marketing as another service for customers.[citation needed] Loral Skynet announced on June 21, 2001 that DMX/AEI would switch from their Telstar 4 to Telstar 8 in 2002.[7] As of 2009, DMX had originally applied to merge with Fort Mill, South Carolina competitor Muzak Holdings LLC, with the resultant combined entity sold to a third-party buyer. Reportedly, Mood Media of Canada had been heavily courted since the beginning, but the combination of the United States Department of Justice's second request for information on the merger,[8] and the bankruptcy filing by Muzak disrupted that original merger.[9] Instead, on Thursday, March 24, 2011, Mood Media themselves announced that they would be buying Muzak in a $345 million deal,[10] and then a year later, Mood Media also announced their acquisition of the original DMX company which had courted them three years earlier on March 19, 2012 in a deal valued at $86.1 million .[11] SonicTap From February 9, 2010 to February 10, 2018, DMX (music) provided over 84 commercial-free audio-only music channels to DirecTV customers, branded as SonicTap .[12][13] DirecTV dropped Sonic Tap in favor of Music Choice on February 10, 2018 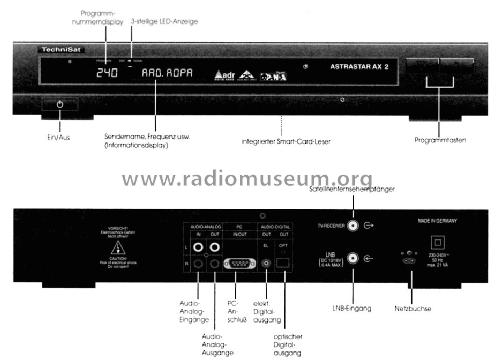
Last edited by svhs; 07-06-2019 at 09:36 AM. |
|
#2
|
||||
|
||||
|
In Norway, ignoring a lot of people's opinion the abolished F.M. ...
Anyway, I didn't knew of the existence of this systems and though only D.A.B. (ha, D.A.B. is also a beer brand! - Germany, and there was a Danish bus builter with tha name too!) was the 1st digital radio system. Last edited by Telecolor 3007; 07-06-2019 at 12:34 AM. |
|
#3
|
||||
|
||||
|
AND the main article
ABANDONED FIRST DIGITAL TV AUDIO SYSTEMS IN JAPAN Transmission method normal image quality Video is analog Band-limited to 4.5 MHz NTSC [14] The presence or absence of scrambling is multiplexed to voice data Multiplexed 15 Hz energy spread signal Frequency shift after FM modulation is 17 MHz Basically, similar to terrestrial analog broadcasting, it also supports teletext and subtitles (only NHK satellite 2nd TV). Voice is digital Normal sound quality 4 channels or high sound quality 2 channels A mode: 32 kHz 14/10 bit quasi-instantaneous decompression × 4 channels (TV audio broadcast 2 channels + independent audio broadcast 2 channels), data broadcast of at least 480 bits per frame B mode: 48 kHz 16 bit linear PCM × 2 ch, data broadcast of at least 224 bits per frame [15] B mode is (theoretically) higher sound quality than CD and BS digital broadcasting and is equivalent to DAT Data broadcasting is performed using the free area of the audio frame If data broadcasting is provided in packet format, it will be 288 bytes / packet [16] Diagonal scanning is performed, and one packet is transmitted in nine frames (one super frame) DQPSK 2048 kbps with subcarrier 5.7272 MHz 2048 bits per frame, 1 millisecond Voice data is protected from transmission errors by (63, 56) BCH codes and 32-bit interleaving FM modulation by mixing video and DQPSK modulated audio data by subcarrier https://translate.google.bg/translat...pling_Encoding Audio compression [17] 1350 bits per frame 1 millisecond Voice compression method: Semi-instantaneous companding DPCM mode A mode: 32 kHz 15-8 bits (8 ranges) x 4 ch (3-1 stereo) B mode: 48 kHz 16-11 bits (6 ranges) x 2 channels Voice error control: (82, 74) shortened BCH 16-bit interleave Multiplexing method: Ternary baseband multiplexing at 12.15 Mbaud during vertical retrace period https://usermanual.wiki/Document/Pan...267423243/html The audio is compressed by the DANCE ( DPCM Audio Near-instantaneous Compression and Expanding ) method developed for MUSE. Unlike standard broadcasts, sampling frequency 32 kHz 15 bits in up to 4 channels A mode supporting 3-1 stereo format, 48 kHz 16 bits digitized voice difference between sample points in up to 2 channels B mode with high sound quality DPCM compression is performed , and the difference signal is subjected to quasi-instantaneous companding (dropping) in a 1 ms interval, and compressed into 8 ranges 8 bits in A mode and 6 ranges 11 bits in B mode. Noise and DC errors at the time of transmission errors are reduced by performing incomplete integration using leak values in DPCM compression performed here, and by providing local decoders, accumulation of compression errors is prevented. This compressed digital voice is protected by (82, 74) shortened BCH and then interleaved by 16 bits, converted from a binary value of 0 and 1 to a ternary value of 0/1/2 12.15 Mbaud · time axis changed and MUSE Store in the vertical blanking interval, the part not displayed on the screen of the image. As for the value at the time of ternarization, the transmission path is different between AM and FM, and in the case of LD , the area for data broadcasting is removed to add stronger error correction [5] [18] . For data broadcasting, a 288-byte packet scheme with diagonal arrangement is adopted as in standard television broadcasting, and 18 frames constitute one super frameBitsream outputs on the MUSE decoders output DANCE audio track in its native form. There are no known AV processors that can decode this format. There are no outboard DANCE decoders either. Most if not all MUSE decoders convert DANCE into 2 pairs of PCM audio. A-MODE tracks are oversampled to 16bit(from 13bit) since PCM doesn't support 13bit. The sampling is untouched at 32Khz. The output is over 2 digital coax/optical. There are no known AV processors which can use two digital coax/optical simultaniously BECAUSE https://translate.google.bg/translat...%2F25%2F091732 When the television receives the BS, it outputs the detection signal and the bit stream signal to the WOWOW decoder . The WOWOW decoder receives the two signals, generates unscrambled video and audio, and outputs video and audio signals from the yellow, white, and red terminals. The television receives video and audio signals from the WOWOW decoder at a dedicated " scramble decoder input terminal". And on the television side, "If you receive BS-5 ch, it is scrambled . So, instead of displaying the video from the BS tuner, let's display the video / audio signal from the scramble decoder input terminal." Process. Now you can watch it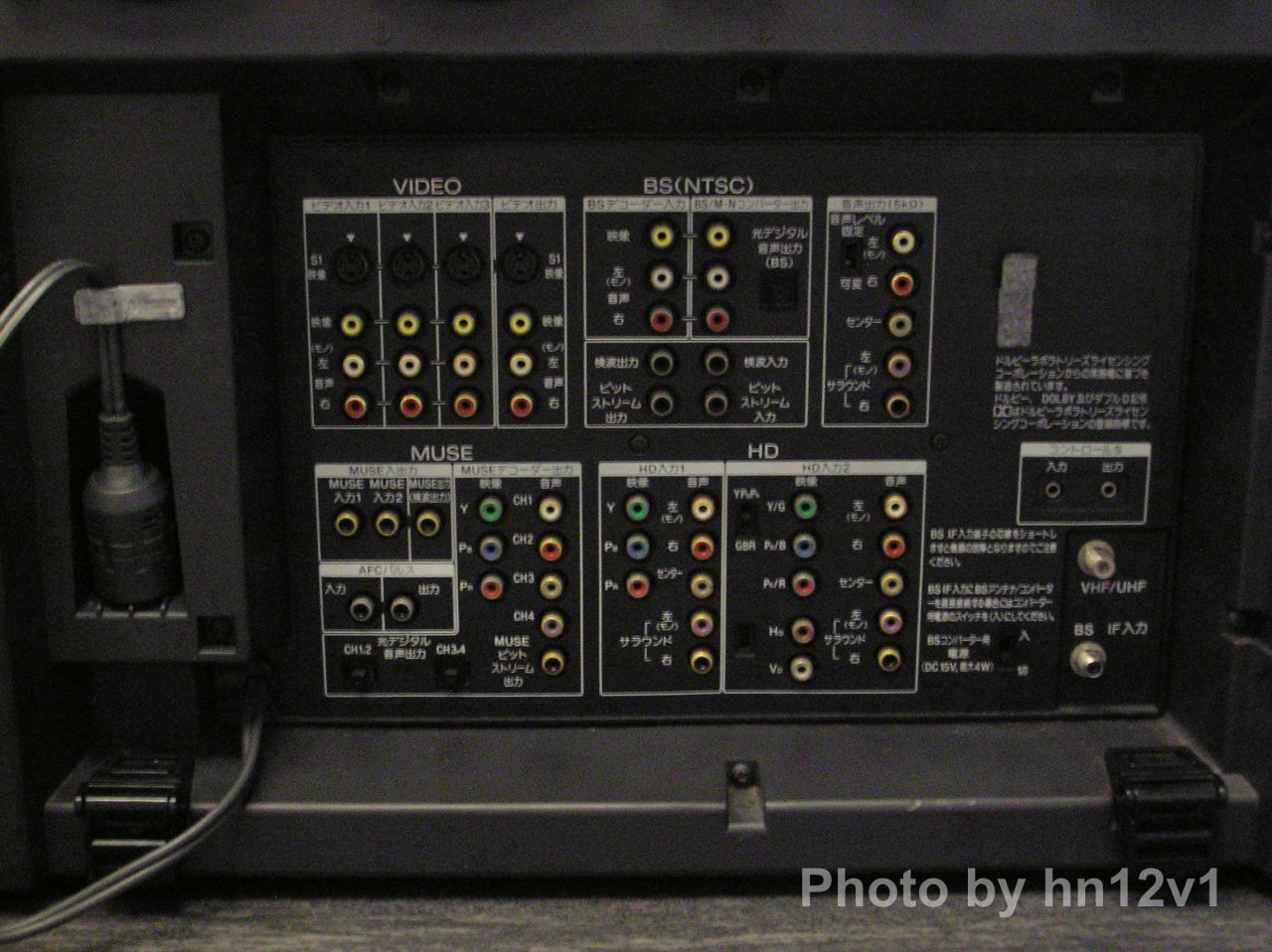      KW-3200HD 1992 KW-3200HD 1992IN EUROPE/WORLD D-MAC (used by British Satellite Broadcasting) but not used on cable systems. This is a satellite only MAC format. Also used by NRK. This because D-MAC has 4 audio channels (D2-MAC just has 2 audio channels). Then it was possible to transmit 3 radio channels and 1 TV channel at one D-MAC channel. NICAM was originally intended to provide broadcasters with six high-quality audio channels within a total bandwidth of 2048 kbit/s. This figure was chosen to match the E1 primary multiplex rate, and systems using this rate could make use of the planned PDH national and international telecommunications networks. Last edited by svhs; 07-15-2019 at 08:37 AM. |
|
#4
|
||||
|
||||
|
Techmoan mentioned DAB a while ago and it's major shortcomings which you described.
I still love how they managed to make the channel selection work using mediocre bitrates and then once the bandwidth improved they just added more mediocre bandwidth stations instead of actually improving on it. It was hinted here about a decade ago that we should also go digital but that bud was nipped pretty fast due to signal issues. |
|
#5
|
||||
|
||||
|
I remember HD radio over AM would mix digital noise in with the analog station making the analog a pain to listen to...I haven't heard that junk on AM in a few years so hopefully it is as dead as I think it is.
FM HD radio seems to not interfere luckily (it also seems there are still HD FM stations).... Never listened to an HD radio register to see if it was any good.
__________________
Tom C. Zenith: The quality stays in EVEN after the name falls off! What I want. --> http://www.videokarma.org/showpost.p...62&postcount=4 |
| Audiokarma |
|
#6
|
||||
|
||||
|
Quote:
__________________
Mom (1938 - 2013) - RIP, I miss you Spunky, (1999 - 2016) - RIP, pretty girl! Rascal, (2007 - 2021) RIP, miss you very much |
|
#7
|
|||
|
|||
|
What! No DRM???
__________________
Rick (Sparks) Ethridge |
|
#8
|
||||
|
||||
|
Man, what's that's tv. I want one!
|
|
#9
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
 |
| Thread Tools | |
| Display Modes | |
|
|